Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems play a crucial role in maintaining indoor air quality and comfort. Whether you are a professional in the field or a homeowner looking to understand more about your system, knowing essential HVAC terms can be beneficial.
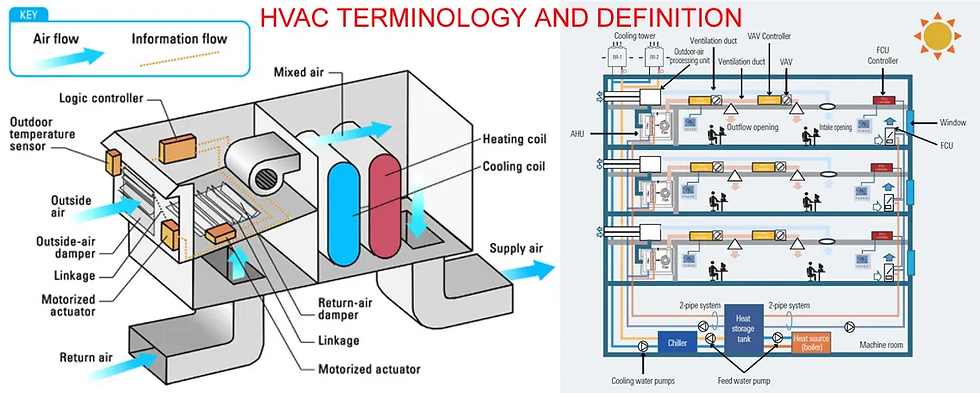
Here’s a comprehensive list of 50 key HVAC terms and their meanings:
1. Air Handler - A unit that circulates and regulates air as part of an HVAC system.
2. BTU (British Thermal Unit) - A measurement of heat energy; one BTU is the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit.
3. CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) - A measurement of airflow volume; indicates the amount of air moved by a system per minute.
4. Compressor - The component in an HVAC system that pressurizes refrigerant to cool or heat a space.
5. Condenser Coil - A heat exchanger that releases heat from refrigerant into the outside air.
6. Ductwork - A network of tubes that distribute air throughout a building.
7. Evaporator Coil - A coil in an air handler that absorbs heat from indoor air.
8. Refrigerant - A chemical compound that absorbs and releases heat to provide cooling and heating.
9. Thermostat - A device that regulates temperature by controlling HVAC systems.
10. SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) - A rating that measures the efficiency of an air conditioning unit.
11. AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) - A measure of furnace efficiency expressed as a percentage.
12. Heat Pump - A device that transfers heat between indoor and outdoor environments for heating or cooling.
13. HVAC Load Calculation - The process of determining the heating and cooling needs of a space.
14. Dehumidifier - A device that removes excess moisture from the air.
15. Humidifier - A device that adds moisture to the air.
16. VAV (Variable Air Volume) - A type of HVAC system that controls airflow based on demand.
17. Zoning System - A system that divides a building into different climate-controlled areas.
18. Air Filter - A component that removes dust and contaminants from the air.
19. Heat Exchanger - A device that transfers heat from one medium to another.
20. ERV (Energy Recovery Ventilator) - A system that exchanges stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air while recovering heat and humidity.
21. HRV (Heat Recovery Ventilator) - Similar to an ERV but focuses on heat exchange without humidity control.
22. Dampers - Adjustable plates that regulate airflow in ducts.
23. Static Pressure - The resistance to airflow in an HVAC system.
24. Blower Motor - A motor that drives the fan in an HVAC system.
25. Capacitor - A device that stores electrical energy to help start HVAC motors.
26. Expansion Valve - A valve that regulates refrigerant flow into the evaporator coil.
27. Condensate Drain - A drainage system that removes excess moisture collected by an HVAC system.
28. Split System - A type of HVAC system with separate indoor and outdoor units.
29. Packaged System - An all-in-one HVAC unit containing heating and cooling components.
30. Thermal Expansion Valve (TXV) - A device that controls refrigerant flow to improve efficiency.
31. HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor) - A measure of heat pump efficiency.
32. MERV (Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value) - A rating system for air filter efficiency.
33. Ductless Mini-Split - A heating and cooling system that does not require ductwork.
34. Radiant Heating - A heating method that transfers heat directly from surfaces to people and objects.
35. Scroll Compressor - A type of compressor known for high efficiency and reliability.
36. Plenum - A chamber in an HVAC system that distributes or collects air.
37. Return Air - Air that is drawn back into an HVAC system for reconditioning.
38. Supply Air - Conditioned air that is delivered to a space.
39. Economizer - A device that uses outside air for cooling when conditions allow.
40. Cycling Rate - The frequency with which an HVAC system turns on and off.
41. Setpoint - The desired temperature setting on a thermostat.
42. Air Balancing - Adjusting an HVAC system for even air distribution.
43. Insulation - Material that reduces heat loss or gain in HVAC systems.
44. Latent Heat - The energy absorbed or released during phase changes, such as condensation or evaporation.
45. Sensible Heat - Heat that changes temperature but not state.
46. Chiller - A machine that removes heat from liquid for cooling applications.
47. Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) - A system that adjusts refrigerant flow to match demand.
48. Two-Stage Compressor - A compressor that operates at two levels for efficiency.
49. Load Shedding - The process of reducing energy consumption during peak demand.
50. Air Changes Per Hour (ACH) - The number of times air in a space is replaced within an hour.
Conclusion
Understanding HVAC terminology is essential for anyone involved in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning. These 50 terms provide a foundation for better communication and decision-making in the field. Whether you are maintaining, repairing, or installing an HVAC system, knowing these terms will enhance your knowledge and efficiency.

Comments