A Comprehensive Guide to Flanges: Essential Components in Mechanical and Piping Systems
- Bk Engineering
- Feb 26
- 4 min read
Updated: 2 days ago
Flanges are crucial components in a wide range of mechanical and piping systems. From maintaining seamless fluid flow to ensuring safety in high-pressure environments, flanges are integral in connecting pipes, valves, pumps, and other equipment. This blog post offers a detailed overview of flanges, covering their types, characteristics, applications, and the machining process that ensures their reliability in various industries
Table Of Content
What is a Flange?
A flange is a flat, disc-like component designed to join or seal pipes, valves, containers, or mechanical parts. Flanges are typically used in pairs and are secured by bolts. A gasket is often placed between the two flanges to form a tight seal, preventing leakage of fluids or gases.
Flanges are essential for maintaining the integrity of piping systems while offering the convenience of easy assembly, maintenance, and modifications.

Key Characteristics of Flanges
Flanges have several defining characteristics that ensure they perform optimally in various systems:
Accurate Drilling: Flanges feature precisely drilled holes to ensure easy and secure assembly.
Controlled Grain Flow: This design enhances the strength and stiffness of the flange.
Machined Bevels: Bevels are machined to facilitate welding, ensuring strong connections.
Smooth Bore: The bore of the flange is smooth to prevent obstructions and maintain flow integrity.
Spot-Facing: Spot-facing ensures fasteners seat securely and squarely.
Material Variety: Flanges are available in different materials, such as stainless steel, cast iron, and plastic, with forged carbon steel being one of the most common.
Standards Compliance: Flanges are designed according to international standards like ASME B16.5 and B16.47 to ensure uniformity and reliability.
Clear Markings: Markings include details such as the manufacturer’s logo, material, pressure rating, and size.
Common Types of Flanges
Each type of flange is designed for specific applications, and understanding these types is crucial for selecting the right flange for your system. Here are some of the most commonly used flange types:
1. Welding Neck Flanges
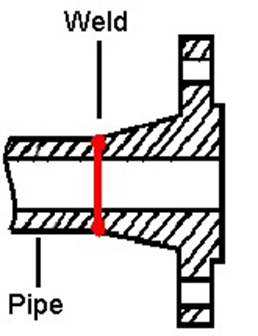

These are best for high-pressure and high-temperature environments. The flange is attached to the pipe using butt welding, ensuring a smooth and unrestricted flow of materials.
Example: Used in oil and gas pipelines that carry highly pressurized fluids.
Welding neck flanges ensure high integrity in pressure and temperature-sensitive applications.
2. Slip-On Flanges
This type of flange is ideal for low-pressure and low-temperature systems. The pipe slips into the flange and is welded on both sides for a secure connection.
Example: Used in HVAC systems where pressure and temperature demands are moderate.


3. Socket Weld Flanges
Socket weld flanges are used primarily for smaller-diameter pipes in high-pressure systems. The pipe is inserted into a socket and welded into place.
Example: Common in steam systems and gas distribution systems.


4. Threaded Flanges

These flanges are screwed onto pipes, making them ideal for smaller dimensions and low-pressure systems. They are often used in applications where welding might not be feasible.
Example: Used in chemical systems where welding could pose a risk due to flammable substances.

5. Blind Flanges
Blind flanges are used to close off the ends of piping systems. These flanges have no opening and are essential when isolating parts of a system or stopping fluid flow.
Example: Used in test systems for pressure testing or in systems under construction.
Blind flanges are used to seal off pipe ends in systems for maintenance or testing.

Flange Faces
The face of a flange plays a significant role in determining the type of gasket needed for sealing. The common flange face types include:
1. Raised Face (RF)
This face type features an elevated portion around the bore and is commonly used in the oil and gas and chemical industries.

2. Male and Female (M&F)
This face includes grooves that match with the female face of the mating flange, helping to hold the gasket securely in place.

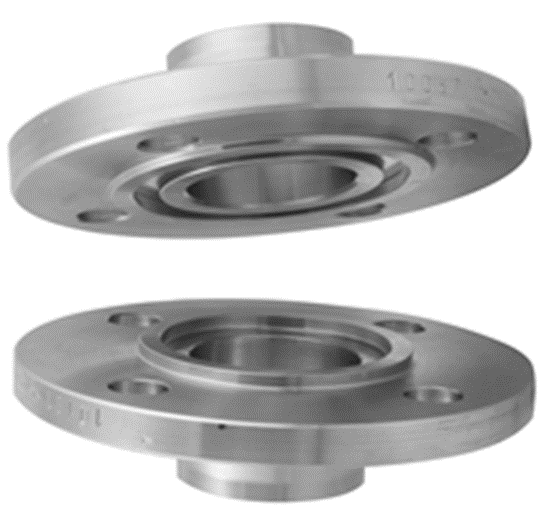
3. Tongue and Groove (T&G)
T&G faces feature a tongue on one flange and a corresponding groove on the other, allowing for self-alignment and easier gasket installation.

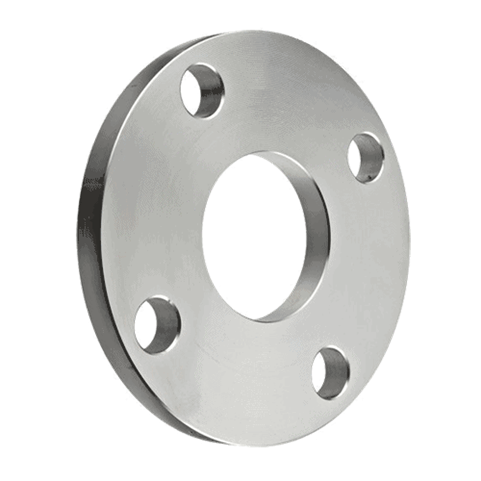
4. Flat Face
A flat face has a simple, flat surface and typically uses a full-face gasket for sealing.

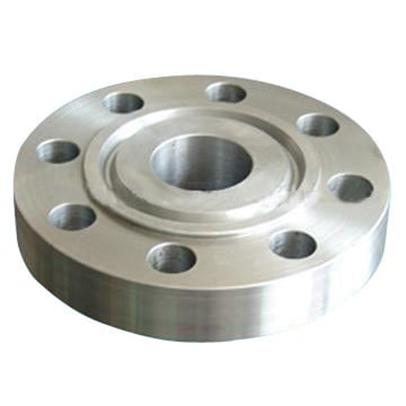
5. Ring Joint Face (RTJ)
Used in high-pressure and high-temperature applications, the RTJ face features a notch for a metal gasket to maintain a tight seal.

Flange Machining Process
The machining process for flanges involves several steps to ensure the flange meets the required specifications:
Material Selection: Materials such as alloy steel, stainless steel, or carbon steel are chosen based on the system's requirements.
Cutting and Shaping: The material is cut into smaller pieces and shaped into the desired flange dimensions.
Heat Treatment: This step improves the mechanical properties of the material, making it more durable.
Forging: The flange is shaped using hot or cold forging techniques.
Machining: Precise dimensions and tolerances are achieved using CNC machines.
Surface Finish: The flange is ground or polished to improve smoothness and remove defects.
Inspection and Quality Control: The finished flanges are thoroughly inspected to ensure they comply with industry standards.
Conclusion
Flanges are indispensable components in modern mechanical and piping systems, ensuring reliable connections, leak-proof seals, and ease of maintenance. By understanding the different types, characteristics, and manufacturing processes, engineers and professionals can select the right flange for their specific needs, optimizing performance, and ensuring safety in their systems.
As industries continue to evolve, the importance of high-quality flanges remains crucial for the successful operation of critical infrastructure across various sectors.


Comentários