Mechanical Engineer's Guide to Jig & Fixture Tool Design
- Bhargava Krishna Marripati
- Feb 20
- 5 min read
Updated: 1 day ago

Table of Content:
Introduction to Jig and Fixture Design
In modern manufacturing, precision and efficiency are crucial. The demand for high-quality products with minimal production errors has made jigs and fixtures indispensable tools in machining and fabrication processes. These specialized devices ensure consistency, reduce manual errors, and enhance productivity by holding and guiding the workpiece securely.

What are Jigs and Fixtures?
Jigs and fixtures are custom-made tools used to hold, support, and locate a workpiece during machining or assembly processes. The primary difference lies in their functionality:
Jigs: Jigs are mainly used to guide cutting tools, ensuring precise positioning of holes and other machining operations. They eliminate the need for marking and measuring on workpieces, thereby improving accuracy and reducing production time.
Fixtures: Unlike jigs, fixtures do not guide the tool but firmly hold the workpiece in a fixed position. They are primarily used in milling, grinding, welding, and turning operations to ensure stability and repeatability.
Difference Between Jigs and Fixtures
Feature | Jigs | Fixtures |
Function | Guides the tool | Holds the workpiece |
Complexity | Generally more complex | Simpler compared to jigs |
Application | Drilling, tapping, reaming | Milling, grinding, welding |
Jigs and fixtures play a critical role in mass production, reducing cycle times, improving worker efficiency, and ensuring consistency across multiple parts.
Fundamentals of Jig and Fixture Design
Jig and fixture design follows fundamental principles that ensure reliability, durability, and ease of use.
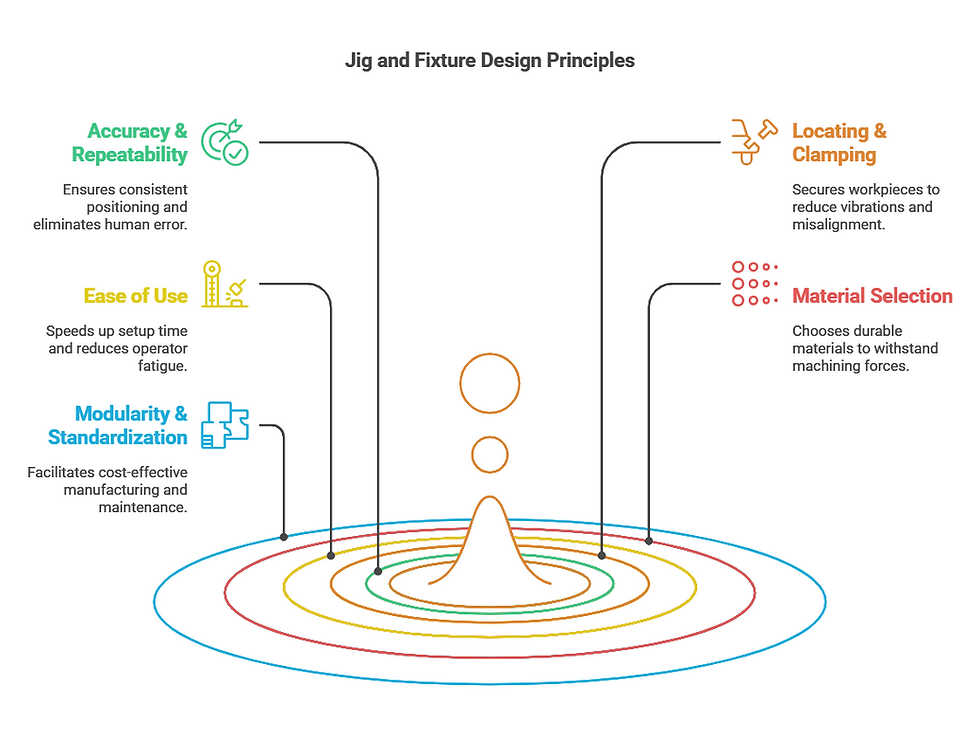
Key Design Principles:
Accuracy & Repeatability: Precision is paramount in manufacturing. A well-designed jig or fixture should guarantee consistent positioning, eliminating variations caused by human error.
Locating & Clamping: Properly securing the workpiece ensures that it remains stationary during machining, reducing vibrations and preventing misalignment.
Ease of Use: A user-friendly design speeds up loading and unloading of workpieces, minimizing setup time and operator fatigue.
Material Selection: Jigs and fixtures are often made from hardened steel, aluminum, or high-strength composites to withstand machining forces without deforming over time.
Modularity & Standardization: Using standardized components such as clamps, bushings, and locating pins makes manufacturing cost-effective and facilitates easy maintenance.
Types of Jigs
Jigs come in various designs, each suited for different machining requirements. The choice of jig depends on the complexity of the operation, the workpiece shape, and the level of precision required.

Template Jig: A simple jig that consists of a template with pre-defined holes used for drilling operations. The operator aligns the drill with the template holes, ensuring accuracy.
Plate Jig: This type of jig includes a plate with drill bushes that guide the cutting tool, reducing wear and tear while improving precision.

Channel Jig: A U-shaped jig that clamps onto the workpiece, providing support and guidance for drilling in restricted areas.
Box Jig: Encloses the workpiece on all sides, ensuring multi-directional machining capabilities.

Angle Plate Jig: Used for machining inclined surfaces, allowing precise angular positioning of the workpiece.

Leaf Jig: Features a hinged top that allows quick loading and unloading of the workpiece without disturbing alignment.

Types of Fixtures
Fixtures are used in a variety of machining and assembly processes. Each type is designed to accommodate specific manufacturing requirements.
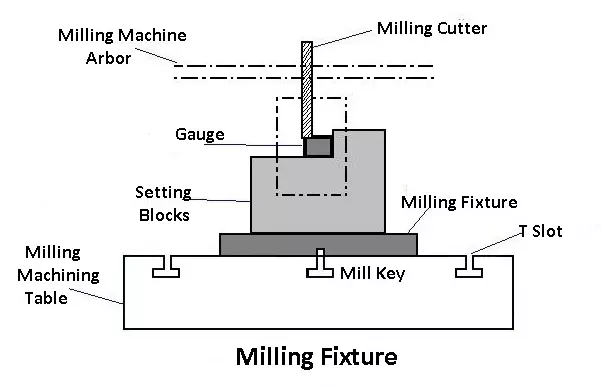
Milling Fixtures: Used to hold workpieces in place during milling operations, ensuring stability and precise cutting paths.
Turning Fixtures: Secure workpieces on lathes, maintaining concentricity and alignment during turning operations.

Drilling Fixtures: Designed to hold and position parts for accurate hole drilling while ensuring uniformity.
Grinding Fixtures: Assist in surface and cylindrical grinding by keeping the workpiece securely positioned against the grinding wheel.
Welding Fixtures: Essential for maintaining alignment in welding operations, preventing distortions caused by heat expansion.
Assembly Fixtures: Facilitate accurate positioning and assembly of components, reducing human error and improving efficiency.
Jig and Fixture Design Process
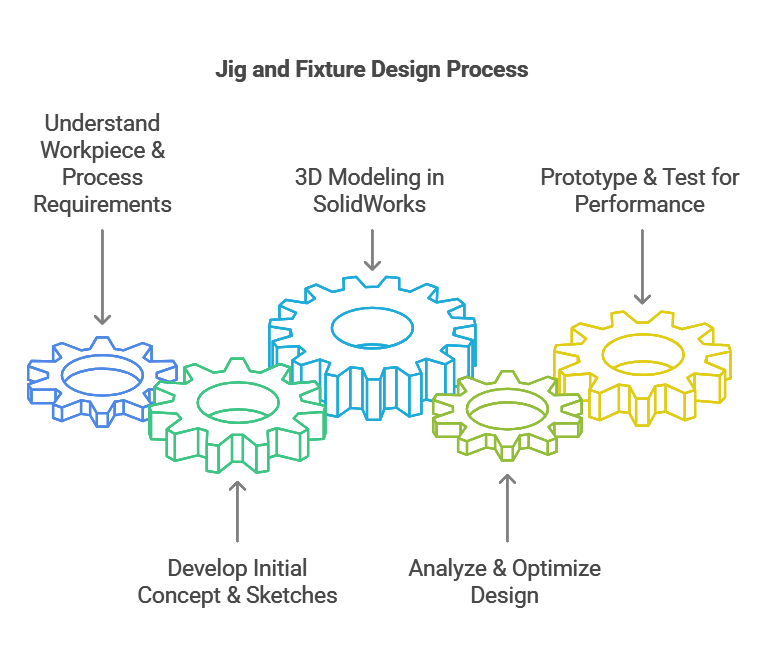
A structured approach to designing jigs and fixtures ensures efficiency and reliability in production. The design process typically follows these steps:
Understand Workpiece & Process Requirements: Analyze the machining process, material properties, and production volume.
Develop Initial Concept & Sketches: Create rough designs considering functionality, ease of use, and manufacturability.
3D Modeling in SolidWorks: Transform sketches into detailed CAD models, incorporating necessary components such as clamps, locators, and supports.
Analyze & Optimize Design: Use Finite Element Analysis (FEA) to test stress distribution and ensure durability under operational loads.
Prototype & Test for Performance: Fabricate a prototype to evaluate real-world functionality and make necessary refinements before final production.
Locating and Clamping Methods
The 3-2-1 principle is a fundamental technique used in jig and fixture design to secure a workpiece in a stable position while minimizing unnecessary movement:
3 Points on one surface restrict movement along the Z-axis.
2 Points on a perpendicular surface restrict movement along the Y-axis.
1 Point constrains the X-axis, completely immobilizing the workpiece.

Common Clamping Methods
Toggle Clamps: Quick and reliable clamping for rapid operations.
Strap Clamps: Provide strong, even pressure distribution.
Pneumatic & Hydraulic Clamps: Automated clamping systems used in high-volume production.
Jig and Fixture Components & Hardware
A well-designed jig or fixture incorporates various components to ensure efficiency:
Bushings: Hardened steel inserts that guide cutting tools and improve tool life.
Dowel Pins: Used for precise alignment of workpieces.
Quick Change Mechanisms: Enable fast setup changes in mass production.
Guide Pins & Supports: Provide additional stability to prevent vibration during machining.
Material Selection Summary Table
Component | Preferred Material | Why? |
Base Plate | Cast Iron, Mild Steel, Aluminum | High strength, vibration damping, durability |
Locating Pins | Hardened Tool Steel, Carbide | High wear resistance, long life |
Bushings | Bronze, Hardened Steel, Carbide | Friction resistance, durability |
Clamps | Spring Steel, Hardened Steel | Toughness, high clamping force |
Fasteners | High-Tensile Steel, Stainless Steel | Corrosion & load resistance |
Surface Coating | Nitriding, Chrome Plating, Anodizing | Improves wear resistance & longevity |
Case Studies & Real-World Examples
Drilling Jig for Aerospace Components: A customized drilling jig helped an aerospace manufacturer improve cycle time by 30%, ensuring uniform hole positioning in aircraft structures.
Welding Fixture for Automotive Frames: A precisely designed fixture was used to hold automotive chassis parts in place, significantly reducing rework due to misalignment.
Milling Fixture for Engine Blocks: A high-precision milling fixture was developed for machining engine blocks, leading to improved consistency and reduced setup time.


Commentaires