Types of Robotic Arms: A Deep Dive Into 6 Groundbreaking Robotic Arm Technologies
- Bhargava Krishna Marripati
- Mar 18
- 10 min read
Updated: 9 hours ago
Table of contents
Introduction to Types of Robotic Arms
Robotic arms, also known as industrial robotic manipulators, are programmable mechanical devices designed to perform various tasks with a high degree of precision, speed, and repeatability. These versatile machines play a crucial role in modern manufacturing processes, assembly lines, and material handling operations.
At their core, robotic arms consist of multiple rigid links connected by joints, allowing for a wide range of motion and dexterity. They can be programmed to perform intricate movements and execute complex tasks with remarkable accuracy. The basic functions of robotic arms include picking and placing objects, welding, painting, assembly, inspection, and a multitude of other applications across various industries.
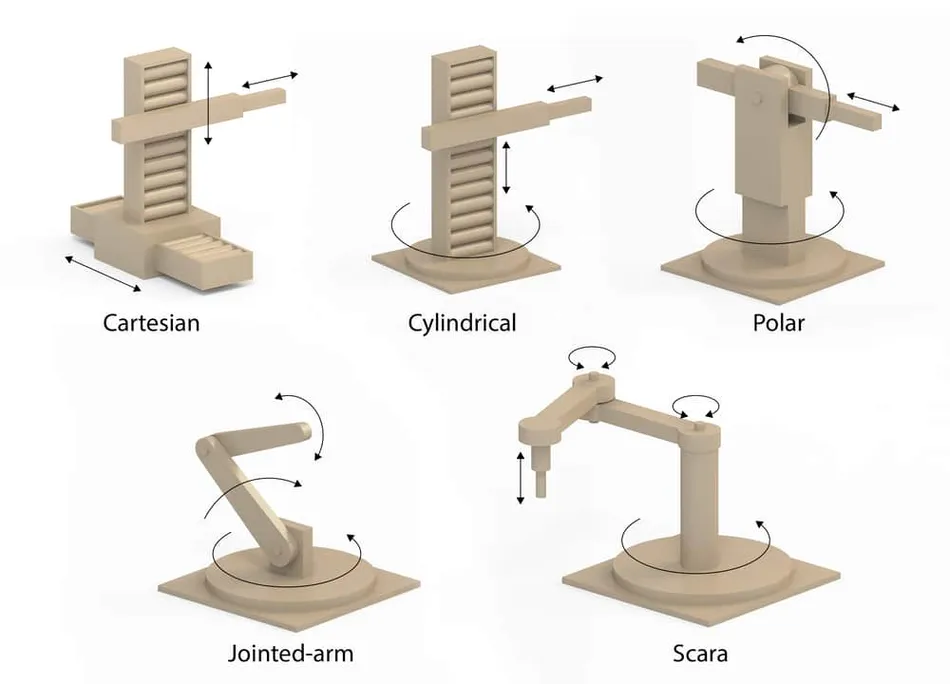
While robotic arms share some common characteristics, they can be categorized into several distinct types, each designed to excel in specific applications and environments. These types of robotic arms include articulated, cartesian, cylindrical, delta, polar/spherical, and SCARA (Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arm) robotic arms, each offering unique advantages and capabilities. [Source: Evolution of robotic arms]
Articulated Robotic Arms
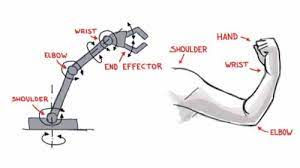
Articulated robotic arms, also known as jointed-arm robots, are among the most versatile and widely used types of industrial robots. They mimic the movement of a human arm, with a series of rotary joints that allow for complex and dexterous motions. This design enables articulated arms to reach and access confined spaces, making them suitable for various applications.
Key features of articulated robotic arms include:
Multiple rotary joints (typically 4-6), providing a high degree of flexibility and maneuverability.
Ability to position the end-effector (gripper, tool, etc.) with a wide range of orientations.
Compact footprint, allowing for efficient use of workspace.
Suitability for handling heavy payloads, depending on the robot's size and configuration.
Articulated arms are commonly used in industries such as automotive manufacturing, where they perform tasks like welding, painting, and material handling. They are also prevalent in electronics assembly, packaging, and machine tending operations. Their versatility makes them adaptable to various applications, from small-scale precision work to heavy-duty material handling tasks. [Source: https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/robotics/robotic-arm.html]
Cartesian Robotic Arms
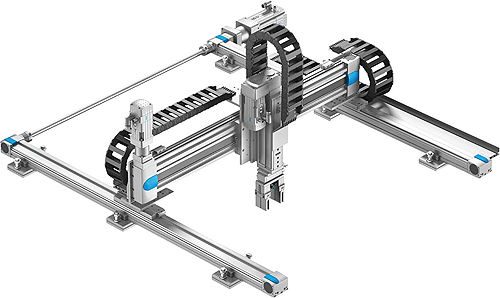
Cartesian robotic arms, also known as linear robotic arms, are characterized by their linear, rectangular movement along the X, Y, and Z axes. This design allows for precise and repeatable motion within a defined three-dimensional workspace. The linear motion is achieved through the use of sliding joints or linear actuators, which enable the arm to move in straight lines along each axis.
One of the key advantages of Cartesian robotic arms is their ability to perform highly accurate and consistent movements, making them well-suited for applications that require precise positioning and repeatability. They are commonly used in manufacturing and assembly lines, where tasks such as pick-and-place operations, packaging, and machine tending are prevalent.
Cartesian robotic arms excel in applications that involve handling large or heavy payloads, as their rigid and sturdy construction provides excellent stability and support. Additionally, their rectangular workspace makes them ideal for tasks that require access to confined or hard-to-reach areas, such as loading and unloading machines or assembling components within tight spaces.
A notable use case for Cartesian robotic arms is in the automotive industry, where they are employed for tasks like welding, material handling, and assembly operations. Their linear motion and precision make them well-suited for these tasks, ensuring consistent and high-quality results. [Source: https://www.universal-robots.com/in/blog/applications-of-robotic-arms/]
Cylindrical Robotic Arms

Cylindrical robotic arms are designed around a single arm capable of moving up and down vertically, as well as rotating around a base and extending or retracting in a linear motion. This configuration allows them to operate within a cylindrical coordinate system, making them well-suited for applications that require access to confined spaces or vertical reaches.
Their compact design and cylindrical workspace make cylindrical robots ideal for material handling, machine tending, and welding tasks. They are commonly found in industries such as automotive, metalworking, and electronics manufacturing, where their ability to reach into tight spaces and perform vertical operations is advantageous. According to Universal Robots, "Cylindrical robots are often used in assembly applications, machine tending, and handling tooling machines where the cylindrical geometry is a good robotic fit."
Delta Robotic Arms

Delta robotic arms, also known as parallel robots, feature a unique design with three parallelogram-shaped arms connected to a central joint. This configuration provides them with exceptional speed and precision, making them ideal for high-speed pick-and-place operations, packaging, and food processing applications.
One of the key advantages of delta robots is their ability to execute up to 300 picks per minute [[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Delta_robot]]. This remarkable speed, combined with their compact footprint, has made them popular choices in factories and production lines where efficiency and throughput are critical.
According to a market research report, the global delta robots market was valued at USD 4.1 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 8.10 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 8.3% [[https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-delta-robots-market]]. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for automation in various industries, as well as the continuous advancements in delta robot technology.
Delta robots excel in applications that require rapid and precise movements within a confined workspace. Their parallel kinematic structure allows for high accelerations and decelerations, making them suitable for tasks such as sorting, assembly, and packaging of small to medium-sized products.
Polar or Spherical Robotic Arms

Polar or spherical robotic arms, also known as polar robots, are characterized by their spherical coordinate system and unique configuration. These robots typically have two rotary joints and one linear joint, allowing them to move in a spherical working envelope.
The polar design consists of a base that rotates around a vertical axis, a shoulder that pivots around a horizontal axis, and an arm that extends or retracts radially. This configuration enables the robot to reach any point within a spherical workspace, making it well-suited for applications that require access to confined spaces or complex geometries.
One of the key advantages of polar robots is their ability to enhance their reach when integrated with a suitably long linear arm. This increased reach can be beneficial in industries such as automotive manufacturing, where access to hard-to-reach areas is crucial for tasks like welding, painting, and material handling.
Typical applications for polar or spherical robotic arms include:
Injection molding
Painting and coating
Arc welding
Spot welding
Machine tending
Material handling
While polar robots offer flexibility and reach, they may have limitations in terms of payload capacity and speed compared to other types of robotic arms. Additionally, their spherical working envelope can pose challenges in terms of workspace optimization and collision avoidance. [Source: https://www.mwes.com/types-of-industrial-robots/polar-spherical-robots/]
SCARA Robotic Arms

SCARA stands for Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arm, a unique design that offers high precision and speed for assembly, packaging, and pick-and-place operations. These robots feature two parallel joints that provide compliance in the X-Y plane and a rigid Z-axis for vertical movement .
The SCARA configuration allows for a compact footprint, making them ideal for applications with limited workspace. They excel at repetitive tasks that require high accuracy and repeatability, such as electronics manufacturing, automotive assembly, and pharmaceutical processing .
Key advantages of SCARA robots include:
High speed and acceleration for rapid cycle times
Excellent precision and repeatability
Flexible deployment in various orientations
Easy integration into existing production lines
Relatively low cost compared to other industrial robots
With their specialized design and capabilities, SCARA robots have revolutionized precision automation in many industries, enabling efficient and cost-effective production processes .
Industries and Applications for Robotic Arms
Robotic arms find extensive applications across various industries, revolutionizing manufacturing processes and enhancing operational efficiency. According to a recent market study [https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2024/11/18/2982819/0/en/Robotic-Arm-Market-Size-to-Worth-USD-81-83-Billion-by-2032-Driven-by-Rapid-Growth-across-Multiple-Industries-Research-by-SNS-Insider.html], the number of active industrial robots is growing at an impressive rate of 14% annually, driven by initiatives like the GermX Initiative.
The automotive industry is a major consumer of robotic arms, leveraging their precision and repeatability for tasks such as welding, painting, and assembly. The electronics industry also heavily relies on robotic arms for precise component placement, soldering, and inspection processes. In the plastics and chemicals sectors, robotic arms are employed for material handling, injection molding, and packaging operations [https://mitsloan.mit.edu/ideas-made-to-matter/a-new-study-measures-actual-impact-robots-jobs-its-significant].
Additionally, robotic arms play a crucial role in industries like food and beverage, pharmaceutical, and aerospace, where they excel at tasks requiring high accuracy, speed, and consistency. Common applications include pick-and-place operations, palletizing, machine tending, and inspection. The versatility of robotic arms also extends to sectors like healthcare, where they assist in surgical procedures, rehabilitation, and laboratory automation.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Robotic Arm

When selecting the right robotic arm for your application, several key factors must be carefully evaluated to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. One crucial consideration is the payload capacity, which refers to the maximum weight the arm can safely lift and manipulate. This is particularly important in material handling, assembly, and manufacturing tasks involving heavy components or products [https://roboticsbiz.com/which-robotic-arm-is-best-for-your-application/].
Another essential factor is the reach or work envelope of the robotic arm, which determines the accessible workspace and the range of motion required for the intended tasks. Certain applications may demand extended reach capabilities, while others may prioritize a more compact footprint for space-saving integration [https://www.moldmakingtechnology.com/articles/10-considerations-for-choosing-a-robot].
Speed and precision are also critical factors, especially in high-speed operations like pick-and-place, packaging, or precision assembly tasks. Different robotic arm types offer varying levels of speed and accuracy, and the specific requirements of your application will dictate the appropriate choice.
Integration with existing systems and equipment is another important consideration. Seamless integration ensures smooth operation, efficient data exchange, and compatibility with other automation components within your facility [https://www.cyient.com/whitepaper/choosing-the-right-ai-enabled-robotic-platform-for-your-business].
Finally, workspace constraints, such as ceiling height, floor space, and potential obstructions, must be taken into account when selecting a robotic arm. The arm's configuration and dimensions should align with the available workspace to avoid interference and ensure safe operation.
Cost Considerations for Robotic Arms
The cost of implementing robotic arms in industrial operations is a crucial factor to consider. According to Standard Robots, the initial investment for a new industrial robot system can range from $20,000 to over $100,000. However, refurbished models are available at roughly half the cost of new systems, offering a more economical option.
Maintenance costs are another essential consideration. Regular maintenance, including software updates, hardware repairs, and consumable replacements, can add to the overall operational expenses. Universal Robots suggests that maintenance costs can account for up to 10-30% of the initial investment over the robot's lifetime.
Despite the upfront and ongoing costs, robotic arms can provide significant cost savings through increased productivity, efficiency, and consistency in operations. Automated processes often lead to reduced labor costs, improved quality control, and minimized waste, ultimately contributing to higher profitability and a faster return on investment.
Trends and Future Developments in Robotic Arm Technology
Robotic arm technology is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, materials science, and sensor technology. One of the most exciting developments is the integration of thought-controlled robotic arms, as demonstrated by Neuralink's revolutionary system [https://www.electropages.com/blog/2024/12/neuralink-prepares-revolutionary-thought-controlled-robotic-arm-study]. This technology allows users to control robotic arms directly with their thoughts, opening up new possibilities for enhancing mobility and independence.
Another area of innovation is the improvement of robot dexterity and the ability to perform complex tasks. Google's DeepMind has made significant strides with systems like ALOHA Unleashed and DemoStart, which enable robots to learn and execute intricate movements with remarkable precision [https://deepmind.google/discover/blog/advances-in-robot-dexterity/]. These advancements have applications in industries ranging from manufacturing to healthcare, where dexterous robotic arms can assist with delicate procedures.
Materials science is also playing a crucial role in the development of robotic arms. Researchers are exploring the use of lightweight yet strong materials, such as carbon fiber composites, to increase payload capacity and energy efficiency. Additionally, the integration of advanced sensors and control systems is enhancing the precision, speed, and responsiveness of robotic arms, allowing for more accurate and efficient operations.
Emerging applications for robotic arms are constantly being explored, with industries like agriculture, construction, and space exploration recognizing their potential. For instance, robotic arms could be used for automated harvesting, assembling structures in hazardous environments, or performing intricate tasks in space missions. As technology continues to advance, the possibilities for robotic arm applications are virtually limitless.
Safety and Regulatory Compliance for Robotic Arms
The integration of robotic arms in industrial settings necessitates stringent safety measures and adherence to industry standards. Ensuring the safe operation of these powerful machines is paramount to protect workers and prevent accidents or injuries.
While there are currently no specific OSHA standards for the robotics industry [http://www.osha.gov/robotics], guidelines have been provided by OSHA for the safe operation and use of robots and robotic systems [http://www.osha.gov/enforcement/directives/std-01-12-002]. Additionally, the ISO 10218-1:2011 standard [https://www.iso.org/standard/51330.html] specifies requirements and guidelines for the inherent safe design, protective measures, and information for use of industrial robots.
Implementing robust safety protocols, such as physical barriers, emergency stop systems, and proper training, is crucial when working with robotic arms. Moreover, as human-robot collaboration becomes more prevalent, it is essential to adopt strategies that enable safe interaction between workers and robotic systems, ensuring a harmonious and productive work environment.
Conclusion
The world of robotic arms encompasses a diverse range of technologies, each with its unique capabilities and advantages. From the versatile articulated arms to the high-speed delta and SCARA designs, the industry offers solutions tailored to meet the specific needs of various applications.
Articulated robotic arms, with their multi-jointed structure, excel in flexibility and dexterity, making them suitable for complex tasks in industries like automotive and electronics manufacturing. Cartesian arms, with their linear motion, are well-suited for assembly lines and material handling, while cylindrical arms shine in welding and machine tending operations.
Delta robots, known for their speed and precision, are invaluable in pick-and-place operations and packaging, while polar or spherical arms excel in coating, dispensing, and reaching confined spaces. SCARA arms, with their rigid yet compliant design, are widely used in assembly, packaging, and electronics manufacturing.
As industries continue to evolve, the demand for robotic arms is expected to grow, driven by their ability to enhance productivity, efficiency, and precision. The future of robotic arm technology promises exciting advancements, such as improved sensors, advanced control systems, and the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities.
With their versatility and potential to transform operations across various sectors, robotic arms stand as a testament to the power of innovation and the pursuit of automation excellence. As businesses seek to stay competitive and optimize their processes, the adoption of these cutting-edge technologies will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of manufacturing and beyond. [Source: https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2024/11/18/2982819/0/en/Robotic-Arm-Market-Size-to-Worth-USD-81-83-Billion-by-2032-Driven-by-Rapid-Growth-across-Multiple-Industries-Research-by-SNS-Insider.html]


Comentarios